Switchgear Committee Annual Report
2014
24-July-2014 (update for PES General Meeting)
Entity: Switchgear Committee
Chair: T. W. Olsen
Vice-Chair: Paul Sullivan
Secretary: Michael Crawford
1. Significant Accomplishments:
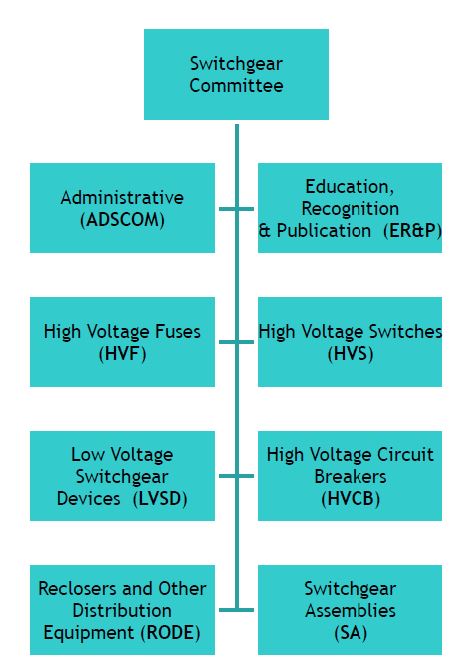
The Switchgear Committee has six technical subcommittees (HV Circuit Breakers, HV Fuses, HV Switches, LV Switchgear Devices, RODE (Reclosers and Other Distribution Equipment, and Switchgear Assemblies), with approximately 35 active working groups or task forces preliminary to formation of working group. The Switchgear Committee has approximately 60 standards. The list of active working groups fluctuates, with working groups disbanded as their projects are completed, and with new working groups forming on a continuing basis.
An active plan is in place to revise any and all relevant standards that are due for administrative withdrawal at the end of 2018, to comply with the changes enacted by IEEE-SA in 2008 that ended reaffirmations and imposed a requirement to revise or withdraw standards that were not revised within ten years of approval.
The Switchgear Committee actively works to harmonize requirements in various standards with the requirements of the relevant IEC standards. At present, requirements for HV circuit breakers are fundamentally harmonized. Requirements for other portions of the Switchgear Committee standards are harmonized with IEC to varying degrees, determined primarily by differences in the user practices between the IEC and ANSI/IEEE markets.
The Switchgear Committee P&P for standards development were accepted by IEEE-SA in December, 2012. The Working Group P&P were created using the PES TechCouncil template in September, 2013, and found to be without issue by AudCom and the IEEE-SA Standards Board in December, 2013. The operating procedures for the committee are in draft form, and it is hoped that formal Committee approval will be obtained at the Fall meeting in September, in Asheville.
During 2013, three standards, guides, or recommended practices updated or created by the Switchgear Committee were published by IEEE-SA. These include:
• C37.121, Guide for Switchgear – Unit Substations – Requirements
• C37.20.4, Standard for Indoor AC Switches (1 kV to 38 kV) for Use in Metal-Enclosed Switchgear
• C37.63, Standard Requirements for Overhead, Pad-Mounted, Dry-Vault, and Submersible Automatic Line Sectionalizers for Alternating Current Systems up to 38 kV.
The Switchgear Committee holds two meetings each year, one in the Spring and one in the Fall. Attendance at these meetings is on an upward trend, rising from around 110 participants in 2003 to 231 participants in Spring, 2014 at the meeting in Orlando. The Switchgear Committee is in sound financial condition. Contracts with hotels for future meetings are in place typically for the next four meetings, and in development for further meetings.
The Switchgear Committee website has been updated to a more interesting format and continues to include access to minutes of past meetings (from 1990 to date), and many technical presentations.
2. Benefits to Industry and PES Members from the Committee Work:
The Switchgear Committee creates and maintains standards that benefit the stakeholders in many ways, including these:
• Users, producers, testing firms, and third-party certification bodies benefit by having performance requirements that are consistent and that give confidence that products carrying equal ratings exhibit equal performance.
• Users and producers benefit by having known performance-oriented requirements rather than rote construction mandated (but not necessarily performance-oriented) requirements. This allows producers to introduce new technologies that produce equal performance without conflicting with arbitrary standards-mandated construction requirements.
• Users, producers, testing firms, and third-party certification bodies benefit from having relatively stable standards for products, as revisions of standards are generally made except at intervals of seven to ten years.
• Users, producers, testing firms, and third-party certification bodies benefit from the creation of new standards covering areas previously not addressed in standards, such as testing of equipment under conditions of internal arcing faults, special interrupting applications such as transformer-limited faults, and conversions of existing equipment to accommodate newer technologies. The guide for internal arcing tests is particularly significant as the document (C37.20.7) has been expanded over the years to cover significantly more equipment varieties, providing a consistent set of testing requirements over a range of product types.
3. Benefits to Volunteer Participants from the Committee Work:
• Participation in standards activities provides a solid basis for education of new participants, while providing a forum to capture the knowledge of experienced participants.
• The Switchgear Committee has participation by a significant number of persons who have formally retired from the business world, yet continue to participate, in several cases without financial support from their former employer or some other firm. It is reasonable to surmise that such individuals would not do so except that participation provides them some measure of satisfaction.
• Participants in the standards process benefit from recognition within their employer organizations as “experts” in their technical field, and particularly if they participate in some officer capacity in working groups or in the committee structure.
• The Switchgear Committee provides recognition to working group members and committee officers, typically with a plaque. When standards are published, the participants are also recognized in the front matter of the document.
4. Recognition of Outstanding Performance:
Education, Recognition, and Publication (ERP) Subcommittee oversees all the activities related to nominations, recognitions, awards, prizes, certificates of appreciations for exceptional individuals and groups. Annually ERP nominates for the following awards:
• PES Prize Paper award
• PES Outstanding WG award
• PES Award for outstanding Standard or Guid
• TC award for prize paper
• TC award for outstanding service to the Committee
• TC award for outstanding Working Group.
In 2013 we nominated:
• Guide for Application Operation and Coordination of HV Current Limiting Fuses (April 2012)- John Leach (Tutorial at IEEE)
• C37.30.1 – Standard Requirements for AC High-Voltage Air Switches Rated Above 1000 V- Carl Weigart- chair
• Steve Lambert, Bill Bergman for individual outstanding TC service awards
• C37.30.1 for TC outstanding WG award.
The Switchgear Committee has had a very high level of quality nominations. For example, in the eight years of PES Prize Papers the Committee’s nominations were awarded six out of eight years (6/8= 75% success rate).
In addition all outgoing officers, including subcommittee chairs, are presented with certificates of appreciation.
ERP also stimulates and encourages nominations for Senior Membership of IEEE and IEEE Fellows.
The Switchgear Chairman, Ted Olsen, was presented with the IEEE-SA Standards Board Distinguished Service Award in December, 2013.
5. Coordination with Other Entities (PES Committees, CIGRE, standards, etc.):
Switchgear Committee keeps a close liaison with CIGRE Study Committee A3 (High Voltage Equipment). Mietek Glinkowski is an official US Representative to CIGRE SC A3 as well as the liaison between IEEE Switchgear Committee and CIGRE A3.
A number of projects and standards are in process or published that are joint efforts with other IEEE PES sponsors or with the IEC. Among these are:
• P62271-37-013, dual logo, IEEE/IEC, High-Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear – Part 37-013: Alternating-current generator circuit-breakers. (nearing completion)
• IEC 62271-111 / IEEE C37.60, dual logo IEEE/IEC, High voltage switchgear and controlgear – Part 111: Overhead, pad-mounted, dry vault, and submersible automatic circuit reclosers and fault interrupters for alternating current systems up to 38 kV. (revision beginning)
• PC37.20.9, Metal Enclosed Switchgear Rated 1kV to 52 kV Incorporating Gas Insulation Systems, co-sponsored by IEEE PES Substations Committee (project starting)
• P1860, Voltage and Reactive Power in 1000kV or Greater (Ultra High Voltage) AC Systems, sponsored by CAG (Corporate Advisory Group), and co-sponsored by IEEE PES Switchgear, Transformers, and Substations Committees. (approved May, 2014).
• P1861 Acceptance Tests on Site Hand-Over Test of 1000kV or Greater (Ultra High Voltage) AC Electrical Equipment and Commissioning Procedures, sponsored by CAG (Corporate Advisory Group), and co-sponsored by IEEE PES Switchgear, Transformers, and Substations Committees. (approved June, 2014)
• P1862 Overvoltage and Insulation Coordination of 1000kV or Greater (Ultra High Voltage) AC Transmission Systems, sponsored by CAG (Corporate Advisory Group), and co-sponsored by IEEE PES Switchgear, Transformers, and Substations Committees. (approved May, 2014
• C37.122, High Voltage Gas-Insulated Substations Rated Above 52kV, sponsored by IEEE PES Substations Committee, co-sponsored by IEEE PES Switchgear Committee.
• IEC 62271-37-082, dual logo, IEEE/IEC, High-voltage switchgear and controlgear – Part 37-082: Measurement of sound pressure levels on alternating current circuit-breakers.
6. New Technologies of Interest to the Committee:
The committee has several projects or task forces involved in new technologies:
• P37.302, Guide for Fault Current Limiter (FCL) Testing. This document describes the testing of fault current limiters operating on condition based impedance increase for AC systems 1000Vac and above. It does not cover such devices as series reactors or current-limiting fuses.
• Task force for solid dielectric equipment, which is exploring materials, application conditions, environmental conditions, and tests for new insulation systems in which insulation is molded as an integral element of an assembly that includes the interrupting or switching device, e.g,, such as for an outdoor distribution recloser. The task force anticipates issuing their final report in the near future.
• Task force for distribution equipment controls is developing a technical report with recommendations for microprocessor-based controls for equipment over 1000Vac up to 38kVac for overhead and underground distribution lines, including test and application information. Such controls typically would include the protection associated with the switching device, as well as the controls devices (open, close, etc.) with communications capability. The control device would serve in place of traditional relays and control devices that are appropriate for high voltage circuit breakers but not suitable for distribution equipment mounted on power poles or below grade.
7. Problems and Concerns:
At present, the Switchgear Committee has no pressing issues and concerns.
• The major issue of the mandated expiration of standards at the end of 2018 seems to be well under control, as plans and projects are in place to address each standard before 2018.
• Creation of acceptable P&P for standards development, including sponsor P&P and working group P&P, has been accomplished. This was a carryover major issue from previous years.
• Relations with IEEE-SA, in sad condition some years ago, are now EXCELLENT, and IEEE-SA staff personnel have been extremely helpful to the Switchgear Committee.
8. Significant Plans for the Next Period:
• Continue to monitor standards scheduled for withdrawal in 2018 to assure that ongoing projects are completed before withdrawal.
• Work with selected subcommittees that have a very heavy workload of standards to be revised to assure that the workload can be handled within the available resources and time. This requires that projects need to be completed within the four year validity of a PAR. Long duration projects, six, eight, or more years in duration, can no longer be supported.
Submitted by: T. W. Olsen
Chair, IEEE PES Switchgear Committee
Date: 24-July-2014